VCP550D Delta Exam Technical lab
This page contains nothing but the Technical lab I created to prepare myself for the VMware VCP550D Delta Exam, to re-certified my VCP5 qualification. This page also contains the notes I've taking during my lab creation and test
This lab is based on vSphere 5.5. To start with, I created several VMs using VMware Workstation 10, and because we are gonna be playing a lot with the virtual environment, I decided to put the vCenter and the DC out, so they don't get affected by we messing around with the infrastructure
I love server core, so I installed the DC and vCenter on Server 2008 R2 server cores, this is how I've done it
Step 1: Prepare the vSphere 5.5 environment for the VCP550D Delta Exam
Okay, on a GUI Server Server 2008 R2, install the ADDS role, then run dcpromo and finally export the settings of the new domain (which I called "kute.local") to a txt file. If you don't want to install AD
1. First of all install the DNS role on Server Core 2008 R2 by running dism /online /enable-feature /featurename:DNS-Server-Core-Role
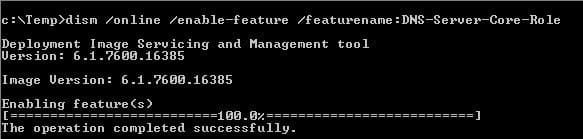
2. Open Notepad and enter this text on it:
[DCInstall]
ReplicaOrNewDomain=Domain
NewDomain=Forest
NewDomainDNSName=kute.local
ForestLevel=4
DomainNetbiosName=KUTE
DomainLevel=4
InstallDNS=Yes
ConfirmGC=Yes
CreateDNSDelegation=No
DatabasePath="C:\Windows\NTDS"
LogPath="C:\Windows\NTDS"
SYSVOLPath="C:\Windows\NTDS"
SafeModeAdminPassword=mySuperSecretPasswd1234##
RebootOnCompletion=Yes
Save the file on the C:\ drive on whatever, and then use it when invoking the dcpromo executable
We also need to install DHCP server, so run this command dism /online /get-features /format:table to see what you got install on the system and then run: dism /online /enable-feature /featurename:DHCPServerCore
To continue with this guide of VCP550D Delta Exam Technical lab, you can now either run this command: sc config dhcp server start= auto not working followed by sc dhcpserver start, or better launch the services.msc console from another computer and connect to our DC to start the DHCP server service.
Staff that is good to know about vCenter Architecture
vFlash Read Cache
- vFlash Read Cache needs:
- Enterprise Plus licensing
- Hardware version 10 on the VM and 5.5 on all the rest (host and vCenter)
- 32TB virtual flash size maximum on host, and 4TB maximum per VMDK
- VFSS is the file system for the SSD drive
- DRS will consider a VM with vFlash as a soft-affinity to the host, and will nto move it unless there is a major unbalanced
- To fake a SSD on your nested lab, add this line to the VMX file of the VM: scsi0:1.virtualsSD = 1
Staff that is good to know about vSphere 5.5 topics for the VCP550D
On the "Tasks & Events" tab, don't forget to click on "Ask WMware" to be re-directed to the VMware knowledge base in certain errors.
In VMHA (High Availability) the Fault Domain Manager Master (FDMS) is elected every time a server reboot, and the host with most mounted datastores is the one that has the better election chances
Stuff god to know for: CLI (Command Line Interface) and ESXi host management
- Some of the useful utilities are:
- vmkping; test connectivity on a vMotion interface
- Some useful commands are:
- Show IP of the host: esxcli network ip interface ipv4 get
- List all the commands: cd sbin and then ls
- List the Ramdisk, using the -h switch provides the percentage: vdf-h
- List the filesystem: df -h
- ESXi Shell is know as "text support mode", while SSH is know as "remote text support mode". On the DCUI (Direct Console User Interface) hold the ALT and press F1 to enter text support mode, press ALT+F2 to go to the DCUIcd
- All log files are located on the ramdisk /tmp/scratch/log/filename.log though they is a symbolic link and you can also see them on /var/log/filename.log ; therefore it is advisable to relocated the Scratch location of the exsi, so that logs are kept not on the temp folder and would be available (persisten logs) after the server reboots; modify the Advanced Setting on each host and configure the scratch location to the shared VMFS store
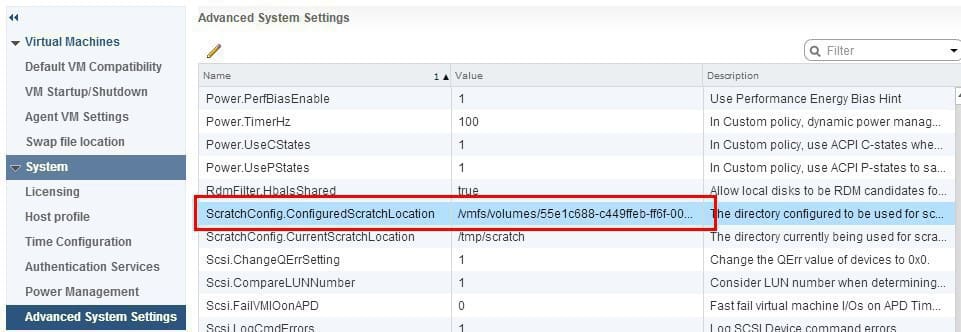
You can install packages on the host (either from VMware -WMwareCertified- or from the third party sources -Partner Supported-), to have a look at the packages installed on the host run: esxcli software vib list ; not that vib stands for vSphere Installation Bundle; every VIB package has a signature according to this that determines the level of support the vib has

vSphere Host Power Management (HPM) can be implemented on ESXi 5.5 hosts to conserve power (do not confuse this with DPM, which works by offline VMs from host and turning hosts idle); HPM works on individual hosts and required specific BIOS configuration so that the host can control the hardware power, basically set the power on the BIOS to "OS control"
To disable Memory Compression Cache (enable by default, which is recommended) set the Mem.MemZipEnable to 0
No VMs can be power on on if they reside on a host specified as a failover host in HA
Stuff god to know for: Creating and dealing with VMs
For the hard drive, choose "LSI Logic SAS" for common purposes VMs, but for VMs in which you're expecting to get more than 2,000 iOPS or more (SQL, Exchange, Oracle, etc) choose "VMware Paravirtual"
To completely disable all the VMware Tools-initiated timey sync functionality, the VMX file of the VM must be modified
Each virtual machine has a memory overhead that is based on the number of vCPUs and memory in the VM
Stuff god to know for: Datastore and AutoDeploy
- When creating VMFS datastores, it is important to maintain a one-to-one (1:1) relationship between each VMFS datasotre and LUN
- VMware advise: If a SAN is connected to the host, detach the Fibre Channel sytem before continuing with the upgrade; do not disable HBA cards in the BIOS
- Remember that UEFI is not supported for Network Boot or AutoDeploy
- For AutoDeploy, configure option 66 on the DHCP server (option 66 is the IP or FQDN of the TFTP server, normally the vCenter) and also option 67, on option 67 you have to enter: undionly.kpxe.vmw-hardwired
- The two iSCSI discovery methods supported by an ESXi host are:
- Static Discovery
- Dynamic Discovery, also known as SendTargets discovery
- The Auto Deploy feature can only exist on one instance per vCenter server
Stuff god to know for: vSphere WebClient
When the Webclient is connected directely to a host, there's only the Events taba to view recent events; tasks are oly shown in the Recent Tasks pane
Stuff god to know for: networking (vSwitch and dvSwitch)
- The Load-balancing policy available only in a dvSwitch is the Route Based On Physical NIC Load, all other load-balancing policies are available in both vSwitch and dvSwitch
- After upgrade to 5.5, don't forget to upgrade the VDS switch to be able to see the new features
- vDSwitch could be either of these two versions:
- Compatible with 5.5 or later:; has these new features available: traffic filtering and marking, and enahnced LACP support
- Compatible with 5.1 or older; has these new features: Management Network Rollback and Recovery, Health Check, Enhanced Port Mirroring and LACP
- To add a dvSwitch, select the Datacenter, then you can add the hosts to the dvSwitch
Stuff god to know for: vCenter
To rollback a failed upgrade of vCenter, proceed as follows:
- Stop vCenter Server
- Restore previous database
- Revert vCenter server
- Start vCenter server
All the certificates for vCenter are kept under ProgramData(%allusersprofiles%) > VMware > VMware VirtualCenter > SSL, this SSL folder definitely should be backup
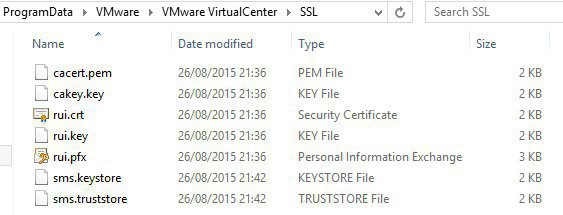
While the certificates for the SSO service (ssoserverSign.crt)are kept under C:\ProgramData\VMware\CIS\cfg\vmware-sso and also in C:\ProgramData\VMware\CIS\runtime\VMwareSTS\conf ; the thumprint needed for vCenter and other services dependent of SSO is on that ssoserverSign.crt file
Remember that the "VMware vCenter Storage Monitoring Profile" service on vCenter needs to run with a domain account and not as the localsystem account
VUM (Update Manager) is used on a 1:1 relationship with vCenter, there can be only 1 x VUM per 1 x vCenter
vCenter Server comes bundled with MS SQL 2002 Express edition, which can only be used up to 5 hosts and 50 VMs in the inventory; vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA) comes with a PostGres database for up to 100 hosts and 3,000 VMs
VCSA needs a DHCP for initial deployment, else manual configuration would be needed
SSO 5.1 uses admin@system-domain while SSO 5.5 uses
For DRS to be enable Enterprise or Enterprise Plus licensing is required, as well as a minimun of 2 hosts and vMotion enable
FT Logging traffic is not encrypted, therefore this network should always be isolated
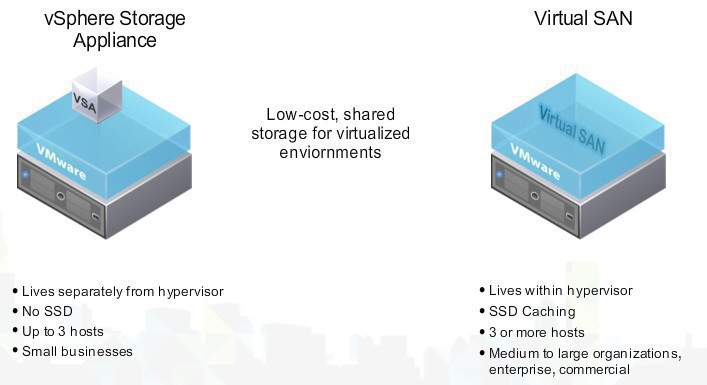
Stuff god to know for: Software-Defined Data Center, (vSAN)
Virtual SAN is not the same as the vSphere Storage Applicance, the big differences are:
Stuff god to know for: know-well ports on vSphere
A reminder of good well-know ports used by vCenter:
- Port 80/443 as well as 8080 /8443 are used for web access
- Port 902 is used for heartbeat, ESXi management and VM console, is required by vCenter Server
- Port 389 is used by LDAP
- Port 514, for TCP and UDP are using for the Syslog Collector
- Port 636 is used for vCenter Linked Mode, in windows this port is used for LDAP too
- Port 1514 is the Syslog Collector SSL secure connection
- Port 6501 used by Auto Deploy Server port
- Port 6502 used by Auto Deploy Management Port
- Port 60099 is used for web service change notification
- Port 10443 is used for vCenter Inventory Service HTTPS
- Port 10109 is used for vCenter Inventory Service Management
- Por 10111 is used for vCenter Inventory Service Linked Mode Communications
Table of IP Addresses:
| No | Server Name | IP Address | Roles and Features |
| 1 | HOST1 | 10.10.10.21 | ESXi 5.5 |
| 2 | HOST2 | 10.10.10.22 | ESXi 6 |
| 3 | SAN1 | 10.10.10.201 | FreeNAS |
| 4 | DC1 | 10.10.10.70 | Domain Controller |
| 5 | vCenter1 | 10.10.10.51 | vCenter |
| 6 | SQL1 | 10.10.10.61 | SQL 2012 |
Tips
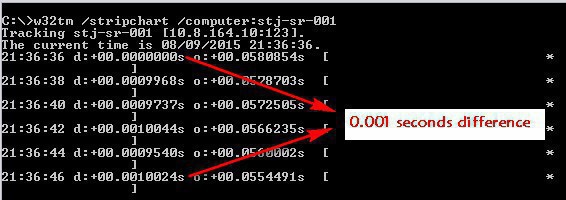
To find out the precise time keeping between a computer and its domain controller, run w32tm /scriptchart /computer:DC1
OPEX = Operating Expenditure, ongoing cost of running a product
CAPEX = Capital Expenditure, incurred when a business spends money to fix an assets or add value to an existing assets
POC = Proof of Concepts
If you liked this article of mine about the VCP550D Delta Exam Technical lab, here there are articles regarding VMware too that you may like! :)
- Certification VCP6 https://www.nazaudy.com/vmware-certified-professional-data-center-virtualisation-vcp6-dcv
- ESXi trunk to Cisco C2960 switch - How to load balance traffic https://www.nazaudy.com/esxi-trunk-to-cisco-c2960-switch-how-to-load-balance-traffic
References
- Correlating VMware product build numbers to update levels (1014508); KB 1014508 to find out who is who http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=1014508
- How VMware ESXi 5.5 determine the order in which names are assigned to devices (2091560); KB2091560 for references, cool stuff http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=2091560
- vCenter Single Sign-On Deployment modes for vSphere 5.5; KB2072435, undestand the concept of SSO and the requirement of high availability for this service http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=2072435
- vCenter SSO 5.5 and interoperability with vSphere 5.1; KB2059249 explains why to use SSO 5.5 instead of 5.1 even if you are running a 5.1 vCenter environment http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=2059249
- Supported vCenter Server high availability options; KB1024051 for your interest http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=1024051
- Enabling Microsoft SQL Clustering Service for vSphere 5.5 and later; KB2059560 for your interest http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=2059560
- Backing up and restoring the vCSA vPostgres database; KB 2034505 for your interest http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=2034505
- Rebuilding indexes to improve the performace of SQL server; KB2009918 for your interest http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=2009918
- Comparing the vSphere Web Client with the fat client; good to know from vmware http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=2095050
- Virtual SAN; as always, great thanks to Duncan Epping for continuing rocking the VMware World http://www.yellow-bricks.com/virtual-san/
- VCP5-DCV Delta done and dusted; thanks to Mark Ukotic for sharing his experience on the Delta exam http://blog.ukotic.net/2014/10/21/vcp5-dcv-delta-done-and-dusted/
- VMware Default Username and Passwords; great stuff compilation by Brian Graf http://www.vtagion.com/vmware-default-username-passwords/
- How to tag disk as SSD VMware ESXi 5.x and 6.0; thanks to Vladan Seget for his insight http://www.vladan.fr/how-to-tag-disk-as-ssd-vmware-esxi-5-x/
- Enabling the SSD option on SSD based disks/LUNs that are not detected as SSD by default; KB 2013188 for your interest http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=2013188
- VSAN; fantastic articles from William Lan http://www.virtuallyghetto.com/vsan
Training Videos:
- Free Self-paced eLearning in Local Languages; with greetings from VMware https://mylearn.vmware.com/mgrReg/plan.cfm?plan=33611&ui=www_edu
- On demand videos from VMUG; great staff from the VMware VMUG community Here is the link to the videos
- vSphere Web Client; good move from VMware; https://www.vmware.com/support/vsphere/vsphere-web-client-video
- Handy Tools:
- RV Tools, gather info from your network environment at a click http://www.robware.net/
- SecureCRT; flexibe ssh to host https://www.vandyke.com/download/securecrt/download.html
- Toolkit 5.5; Thanks to Derek Seaman for such gret scripts http://www.derekseaman.com/2014/01/vsphere-5-5-toolkit-v1-55-released.html
- AutoLab; thanks to they guys/gals at LabGuides; http://www.labguides.com/autolab/autolab-download/?submissionGuid=c2486d94-bd02-4fa2-ac86-a7d47bd483f0
London, 20 September 2015